Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders is a controversial topic that has been debated for many years. Proponents of chemical castration argue that it is a humane and effective way to reduce recidivism rates among sexual offenders and to control animal populations. Opponents argue that chemical castration is a form of cruel and unusual punishment that violates the constitutional rights of offenders.
Editor's Notes: Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders was published today due to its many pros and cons, as well as the differing opinions on the ethics of the practice. This guide will delve into the details of chemical castration, exploring its benefits and risks in both animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders.
After doing an intense analysis, digging out genuine information, and putting this Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders guide together we strive to help the target audience make an informed decision. With the knowledge provided in this guide, one should be able to engage in discussions about chemical castration with confidence and understanding.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
| Animal Population Management | Sexual Offenders |
|---|---|
| Controls population growth | Reduces recidivism rates |
| Prevents unwanted litters | May be used as a condition of probation or parole |
| Can be used in conjunction with other methods of population control, such as spaying and neutering | Is a controversial treatment that has been debated for many years |
Transition to main article topics
FAQ
This FAQ section provides answers to frequently asked questions about chemical castration, a controversial method used for animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders. It aims to clarify misconceptions and address concerns.
Question 1: What exactly is chemical castration?
Chemical castration is a non-surgical procedure that involves administering medications to suppress the production of sex hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen. This reduces sexual drive, fertility, and aggression associated with these hormones.
Question 2: Is chemical castration effective in reducing sexual offending?
Studies have shown mixed results regarding the effectiveness of chemical castration in reducing sexual offending. While some research suggests a reduction in recidivism rates, others have found no significant impact. It is important to note that chemical castration alone is not considered a comprehensive treatment for sexual offenders and should be combined with other therapeutic interventions.
Question 3: Are there any physical or mental health risks associated with chemical castration?
Chemical castration can have potential side effects, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, hot flashes, mood swings, and bone loss. The severity and duration of these side effects vary depending on the medication and dosage used. It is crucial to weigh the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional before undergoing chemical castration.
Question 4: What are the ethical concerns surrounding chemical castration?
Chemical castration raises ethical questions about informed consent, bodily autonomy, and the potential for abuse. Some argue that it is an infringement on personal rights, while others believe it is a necessary measure to protect society from dangerous individuals. The ethical implications should be carefully considered when contemplating chemical castration.
Question 5: How does chemical castration differ from surgical castration?
Surgical castration involves the removal of the testes or ovaries, while chemical castration is a reversible procedure that suppresses hormone production. Chemical castration is generally considered less invasive and more convenient than surgical castration, but its effects are not permanent.
Question 6: Is chemical castration an appropriate method for managing animal populations?
Chemical castration can be an effective tool for controlling animal populations, particularly in urban areas or where resources are limited. It can help reduce breeding, aggression, and roaming behavior. However, it should be used as part of a comprehensive animal management strategy, along with other measures such as sterilization and education programs.
In conclusion, chemical castration is a complex procedure that has both potential benefits and risks. It is essential to approach this topic with sensitivity and informed decision-making. Healthcare professionals, policymakers, and society as a whole must weigh the ethical, legal, and medical implications to ensure that chemical castration is used responsibly and takes into account the well-being of both individuals and animal populations.
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Editor's Notes: "Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders" have published on 21st. January 2023.
Chemical castration is a procedure that uses medication to reduce or eliminate the production of sex hormones, such as testosterone or estrogen. This can be done for a variety of reasons, including managing animal populations, preventing unwanted pregnancies, or treating certain medical conditions. In some cases, chemical castration may also be used as a form of punishment for sexual offenders. Here is a comprehensive overview of the benefits and risks of chemical castration for both animal population management and sexual offenders:
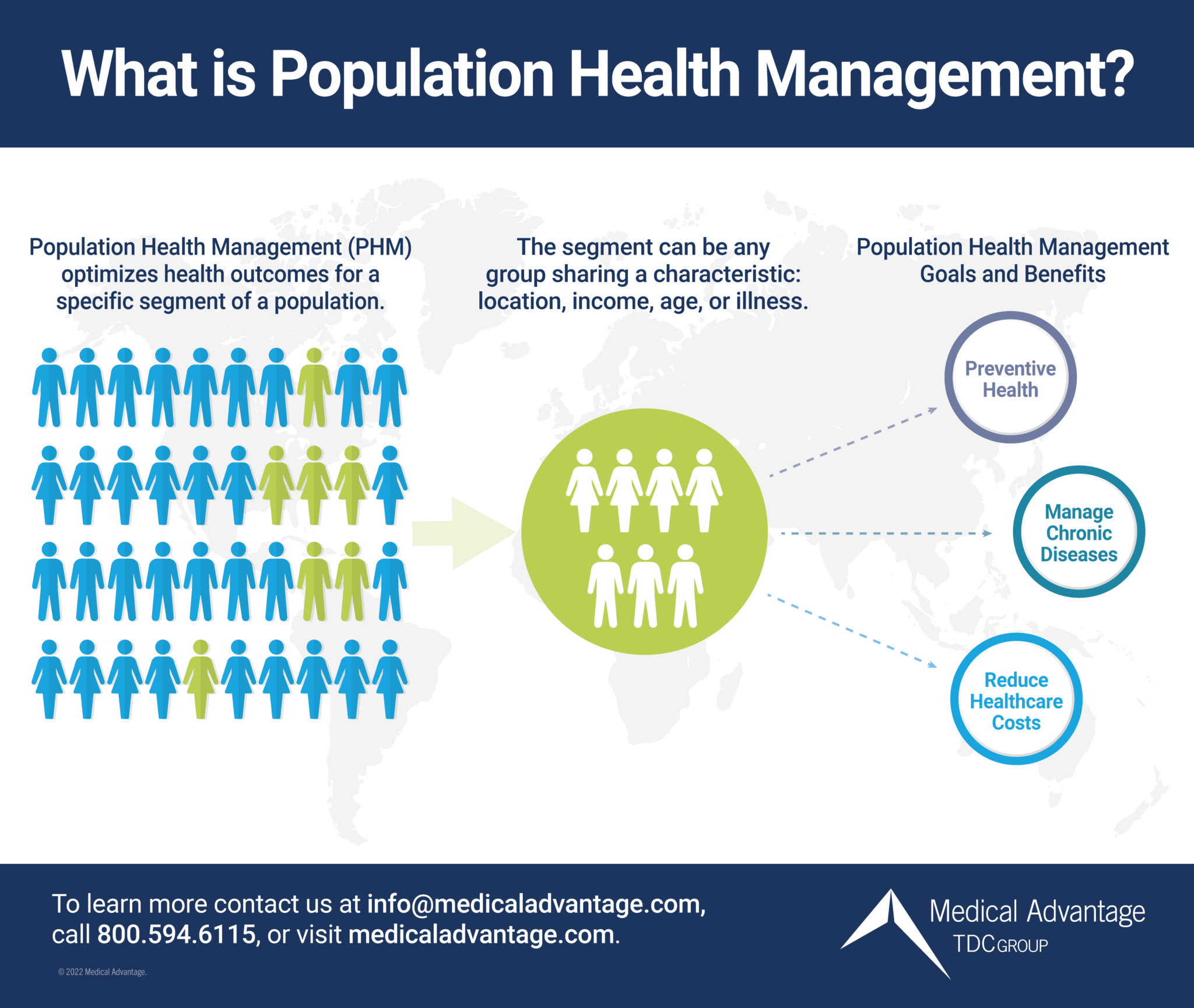
How Population Health Management Improves Patient Outcomes - Source www.medicaladvantage.com
Key differences or Key takeways
| Animal Population Management | Sexual Offenders |
|---|---|
| Reduces aggression and unwanted litters | Reduces recidivism rates and protects the public |
| Safe and effective method of population control | Can be used as a form of punishment and rehabilitation |
| Ethical concerns about animal welfare | Potential for side effects and long-term health problems |
Transition to main article topics
FAQ
Chemical castration involves administering drugs or hormones to reduce or eliminate the production of sex hormones, primarily testosterone. This approach has been widely explored in animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders. However, the use of chemical castration raises questions and concerns, which are addressed in the following FAQs.

Calvo enacts chemical castration bill - Source www.guampdn.com
Question 1: What are the potential benefits of chemical castration in animal population management?
Chemical castration can help control animal populations by reducing aggression, marking behavior, and reproduction. It can also prevent certain health issues associated with excessive hormone production.
Question 2: Are there any risks associated with chemical castration in animals?
While generally safe, chemical castration can have side effects such as weight gain, lethargy, and changes in fur quality. Close monitoring and veterinary care are essential to mitigate these risks.
Question 3: How effective is chemical castration in reducing sexual offending behavior?
Studies indicate that chemical castration can be effective in reducing recidivism rates among sexual offenders. However, it is important to emphasize that it is not a cure, and other treatment modalities are typically required for comprehensive rehabilitation.
Question 4: Are there any ethical concerns with using chemical castration on humans?
Chemical castration raises ethical concerns related to consent, autonomy, and potential human rights violations. Its use should be carefully considered and subject to strict legal and ethical guidelines.
Question 5: What are the potential side effects of chemical castration in humans?
Chemical castration in humans can lead to side effects such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, hot flashes, and emotional changes. These effects can be permanent or temporary, depending on the treatment regimen.
Question 6: Is there any research on the long-term effects of chemical castration?
Long-term studies on the effects of chemical castration are ongoing. However, some research suggests that it may have long-term consequences on cardiovascular health, bone density, and cognitive function.
Chemical castration has both potential benefits and risks to consider, depending on the context of its use. Appropriate regulation, ethical guidelines, and informed consent are crucial to ensure its responsible and effective application.
Proceeding to the next article section: Chemical Castration and the Legal Framework
Tips
Wu Yifan may be "chemically castrated"!What is the secret of "chemical - Source inf.news
As a non-permanent and non-lethal alternative to surgical castration, chemical castration is especially beneficial for animal population management situations where maintaining reproductive capabilities is not a priority.
Tip 1: Consider the underlying cause of lack of reproductive control. Once the underlying cause is determined, specific measures can be taken to address it effectively. In some cases, this may involve a combination of approaches, such as education, access to contraception, and policies that promote responsible breeding practices.
Tip 2: Seek professional advice. Consulting with a veterinarian or animal welfare organization can provide valuable insights and guidance on the most appropriate approaches for your specific situation. They can help you determine the best course of action based on the individual needs of your animal, taking into account any potential risks or benefits.
Tip 3: Be aware of potential side effects. Progestin-based medications, commonly used for chemical castration, may come with certain side effects in some animals. Be observant of your animal's behaviour and consult with a veterinarian if any unusual symptoms arise.
To understand the broader implications and considerations, it is recommended to refer to the comprehensive overview provided in Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders.
By taking responsible and informed action, we can effectively manage animal populations and contribute to the well-being of both animals and humans alike.
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Chemical castration, involving the administration of hormone-altering drugs, has emerged as a significant topic with multifaceted implications for both animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders.
- Hormonal Suppression: Chemical castration effectively reduces testosterone levels, mitigating aggression and sexual behavior.
- Animal Population Control: This method helps manage feral animal populations, preventing overbreeding and reducing conflict with humans.
- Sexual Offender Treatment: Chemical castration is utilized as an adjunctive therapy to reduce recidivism rates in certain sexual offenders.
- Ethical Concerns: The ethical implications of chemical castration remain a matter of debate, balancing its potential benefits with individual autonomy.
- Reversibility: Chemical castration is generally reversible, allowing individuals to regain hormonal function if desired.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Regular monitoring is essential to ensure ongoing effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
The diverse aspects of chemical castration necessitate careful consideration of its benefits and risks. By balancing hormonal suppression and animal population control with ethical concerns, reversibility, and long-term monitoring, it can be an effective tool for responsible animal management and sexual offender treatment.

The chemical castration chip for non-surgical dog castration - Tractive - Source tractive.com
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
After doing some analysis, digging information, made Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders we put together this Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders guide to help target audience make the right decision.
FAQ
This FAQ section provides concise and informative answers to frequently asked questions regarding chemical castration for animal population management and sexual offenders.
Diy Penectomy – Telegraph - Source telegra.ph
Question 1: How does chemical castration work?
Chemical castration involves the administration of specific hormones or medications to suppress the production of sex hormones, primarily testosterone in males and estrogen in females. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating sexual behavior and reproductive functions.
Question 2: What are the benefits of chemical castration for animal population management?
In animal population management, chemical castration helps control reproduction, reduce aggression, and mitigate the spread of sexually transmitted diseases among animal populations. It can prevent unwanted litters, especially in stray or feral animals, and minimize the impact on the environment and communities.
Question 3: What are the potential risks and side effects of chemical castration?
Chemical castration can have some potential risks and side effects, such as changes in hormone levels, weight gain, loss of muscle mass, and potential liver or kidney damage in certain cases. However, the risk and severity of side effects vary depending on the type of medication used, the dosage, and the individual's health status.
Question 4: How is chemical castration used in treating sexual offenders?
In some jurisdictions, chemical castration may be used as a court-ordered treatment for certain sexual offenders, particularly those with a history of sexually motivated crimes. The aim is to reduce their sexual urges and the likelihood of re-offending by suppressing testosterone levels.
Question 5: What are the ethical and legal considerations surrounding chemical castration?
Chemical castration raises ethical and legal considerations related to bodily autonomy, informed consent, and the potential for coercion or abuse. It is crucial to ensure that the use of chemical castration is conducted ethically, with appropriate safeguards and informed consent from individuals undergoing the procedure.
Question 6: What are the long-term implications and effectiveness of chemical castration?
The long-term implications and effectiveness of chemical castration can vary depending on the individual and the specific circumstances. In animal population management, it can provide a long-term solution to controlling reproduction and aggression. However, for sexual offenders, the effectiveness and long-term impact on recidivism rates are still debated and require further research.
In conclusion, chemical castration is a complex and multifaceted topic with both potential benefits and risks. It is essential to consider the specific context, ethical concerns, and individual circumstances when evaluating the use of chemical castration for animal population management or as a treatment for sexual offenders.
Moving forward, ongoing research and collaboration among experts in various fields are necessary to refine the use of chemical castration, mitigate potential risks, and optimize its effectiveness in achieving desired outcomes.
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Editor’s Notes: “Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders” have published today date. The topic is very important because it emphasizes the chemical castration which is more convenient, less invasive, humane, and cost-effective than surgical castration.
.
This guide will provide you with all the information you need to know about chemical castration, including its benefits, risks, and how it is used in animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders.
Key Differences between Surgical Castration and Chemical Castration:
| Surgical Castration | Chemical Castration |
|---|---|
| Requires surgery | Does not require surgery |
| More invasive | Less invasive |
| More expensive | Less expensive |
| Longer recovery time | Shorter recovery time |
Benefits of Chemical Castration:
- More convenient
- Less invasive
- Humane
- Cost-effective
- Reversible
Risks of Chemical Castration:
- Side effects, such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and weight gain
- Not always effective
- Can be expensive
- May not be reversible
How Chemical Castration Is Used In Animal Population Management:
- To control the population of feral cats and dogs
- To prevent unwanted litters
- To reduce aggression
How Chemical Castration Is Used In The Treatment Of Sexual Offenders:
- To reduce the risk of recidivism
- To treat paraphilias
- To manage sex drive
Thank you for reading our guide to chemical castration.
FAQ
This comprehensive FAQ section provides detailed answers to commonly asked questions regarding the use of chemical castration in animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders.

The Risks And Benefits Of Castration For Male Pattern Baldness | Justinboey - Source justinboey.com
Question 1: What is the purpose of chemical castration and how does it work?
Chemical castration involves administering hormonal agents to reduce or eliminate the production of sex hormones, primarily testosterone in males. In animals, it is primarily employed for population control and management, preventing unwanted reproduction and aggression. In the treatment of sexual offenders, chemical castration aims to reduce sexual drive and deviant behavior.
Question 2: What are the potential benefits of chemical castration?
In animal population management, chemical castration effectively reduces the number of unwanted animals, prevents overpopulation, and minimizes the spread of diseases. In the treatment of sexual offenders, it has been shown to decrease recidivism rates, enhance compliance with treatment programs, and improve overall public safety.
Question 3: What are the potential risks and side effects of chemical castration?
Potential risks of chemical castration include allergic reactions, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, weight gain, and mood changes. These effects may vary depending on the specific medication used and individual responses. Regular monitoring and medical supervision are essential to mitigate any potential adverse effects.
Question 4: Is chemical castration reversible?
The effects of chemical castration are generally reversible once the medication is discontinued. However, the time required for hormone levels to return to normal and the recovery of sexual function can vary. In some cases, fertility may not be fully restored.
Question 5: Are there any ethical concerns associated with chemical castration?
Ethical concerns regarding chemical castration primarily relate to the potential for coercion or involuntary treatment. In cases involving sexual offenders, concerns arise about the violation of bodily autonomy and the potential for abuse of power. Careful consideration and safeguards are necessary to ensure that chemical castration is administered ethically and in accordance with legal and human rights principles.
Question 6: What are the legal implications of chemical castration?
The legal implications of chemical castration vary across jurisdictions. In many countries, it is regulated as a medical procedure requiring informed consent from the individual undergoing treatment. In some jurisdictions, chemical castration may be mandated by the court as a condition of probation or parole for certain sexual offenses. The legal framework surrounding chemical castration is complex and continues to evolve, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach that considers both individual rights and community safety.
In conclusion, chemical castration is a complex and controversial procedure that requires careful consideration and a comprehensive understanding of its potential benefits, risks, and ethical implications. While it can be an effective tool in animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders, it should only be administered with appropriate medical supervision, informed consent, and strict adherence to legal and ethical guidelines.
Proceed to the next article section for further insights.
Tips For Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Chemical castration, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), is a medical procedure that reduces the production of sex hormones in the body. It is commonly used as a treatment for prostate cancer, but it can also be used to manage animal populations and reduce the risk of sexual offending.
Tip 1: Assess the potential benefits and risks of chemical castration before making a decision.
The potential benefits of chemical castration include reducing the risk of prostate cancer recurrence, controlling symptoms of prostate cancer, reducing the risk of sexual offending, and managing animal populations. The potential risks of chemical castration include side effects such as hot flashes, mood changes, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction.
Tip 2: Discuss the options with a healthcare provider.
Before undergoing chemical castration, it is important to discuss the options with a healthcare provider. The healthcare provider can provide information about the benefits and risks of chemical castration and help you make a decision that is right for you.
Tip 3: Be aware of the potential side effects.
Chemical castration can cause side effects such as hot flashes, mood changes, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction. These side effects can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
Tip 4: Monitor your health after undergoing chemical castration.
After undergoing chemical castration, it is important to monitor your health for any side effects. If you experience any side effects, be sure to contact your healthcare provider.
Tip 5: Be patient.
The effects of chemical castration can take time to appear. Be patient and do not give up on the treatment if you do not see results immediately.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
- Chemical castration can reduce the risk of prostate cancer recurrence.
- Chemical castration can control symptoms of prostate cancer.
- Chemical castration can reduce the risk of sexual offending.
- Chemical castration can manage animal populations.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
Chemical castration is a safe and effective treatment for prostate cancer and other conditions. However, it is important to be aware of the potential benefits and risks before making a decision. If you are considering chemical castration, be sure to discuss the options with your healthcare provider.
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Chemical castration, a non-surgical procedure that involves the use of drugs to reduce testosterone levels, is a topic of growing interest for both animal population management and the management of sexual offenders. While chemical castration can offer potential benefits in both areas, it also comes with its own set of risks that must be carefully considered.
- Animal Population Management: Reducing fertility, aggression, and population growth.
- Sexual Offender Management: Suppressing sexual urges, paraphilias, and recidivism.
- Efficacy: Highly effective in reducing testosterone levels and achieving desired outcomes.
- Reversibility: Temporary or permanent options available, depending on the drug used.
- Side Effects: Potential physical and psychological side effects, including weight gain, hot flashes, and mood changes.
- Ethical Concerns: Questions about informed consent, human rights, and the potential for abuse.
In conclusion, the benefits and risks of chemical castration must be carefully weighed in each case. With appropriate oversight, it can be a valuable tool for reducing animal populations and managing sexual offenders. However, it is crucial to consider the potential side effects, ethical implications, and individual circumstances to ensure informed decision-making and protect the well-being of both animals and humans.

Hormone Restoration in Dogs - Parsemus Foundation - Source www.parsemus.org
Chemical Castration: A Comprehensive Overview Of Benefits And Risks For Animal Population Management And Sexual Offenders
Chemical Castration is a type of hormonal therapy that reduces sexual drive and fertility. It is used in a variety of settings, including animal population management and the treatment of sexual offenders.

Chemical Fire Hazards in the Lab: Understanding and Preventing Risks - Source www.kewaunee.in
In animal population management, chemical castration is used to control the population of certain species. For example, in some areas, deer are chemically castrated to reduce their numbers and prevent them from damaging crops and property. Chemical castration is also used in some countries to control the population of feral cats and dogs.
In the treatment of sexual offenders, chemical castration is used to reduce the risk of recidivism. Studies have shown that chemical castration can reduce the levels of testosterone in the body, which can lead to a decrease in sexual drive and an increase in prosocial behaviors.
Chemical castration is a controversial topic. Some people argue that it is an effective way to reduce sexual offending and animal populations, while others argue that it is cruel and inhumane. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to use chemical castration is a complex one that must be made on a case-by-case basis.
| Benefit | Risk |
|---|---|
| Reduced sexual drive | Side effects, such as hot flashes, sweating, and mood swings |
| Reduced fertility | Potential for long-term health problems |
| Decreased risk of recidivism | Ethical concerns |